Have you ever noticed how the hottest new gadget always costs a fortune at launch but gets cheaper just months later?
That’s no accident.
Price skimming is the strategic art of launching products at premium prices before gradually lowering them over time.
It’s how Apple sells millions of iPhones at top dollar before introducing more affordable options, and how Tesla captured both luxury buyers and mainstream consumers with a carefully orchestrated pricing cascade.
Some call it opportunistic. Others see it as a brilliant business strategy.
When executed thoughtfully, a skimming price approach maximizes revenue from different customer segments throughout a product’s lifecycle. It captures premium-seeking early adopters first before expanding to more price-sensitive markets.
Today, we’ll discuss price skimming advantages and disadvantages, price skimming examples from market leaders, and advanced tactics that leverage consumer psychology and AI to perfect your pricing strategy.
What Is the Definition of Price Skimming?
Price skimming is a pricing strategy in which companies set the highest possible price for a new product at launch and gradually lower it over time to target different customer segments.
Think of it like skimming cream from the top of milk. You start by collecting the richest part (premium-paying customers) before moving to the next layer (mainstream buyers).
A well-executed skim pricing strategy follows a predictable pattern:
- Launch with higher prices targeting innovation-hungry early adopters.
- Gradually lower prices as the market matures and competitors enter.
- Eventually reach a stable price point that balances profitability and market share.
- Potentially introduce a replacement product to restart the cycle.
Unlike random discounting, price skimming uses an intentional, phased approach to price reduction—each drop carefully timed to capture maximum value from different customer segments.
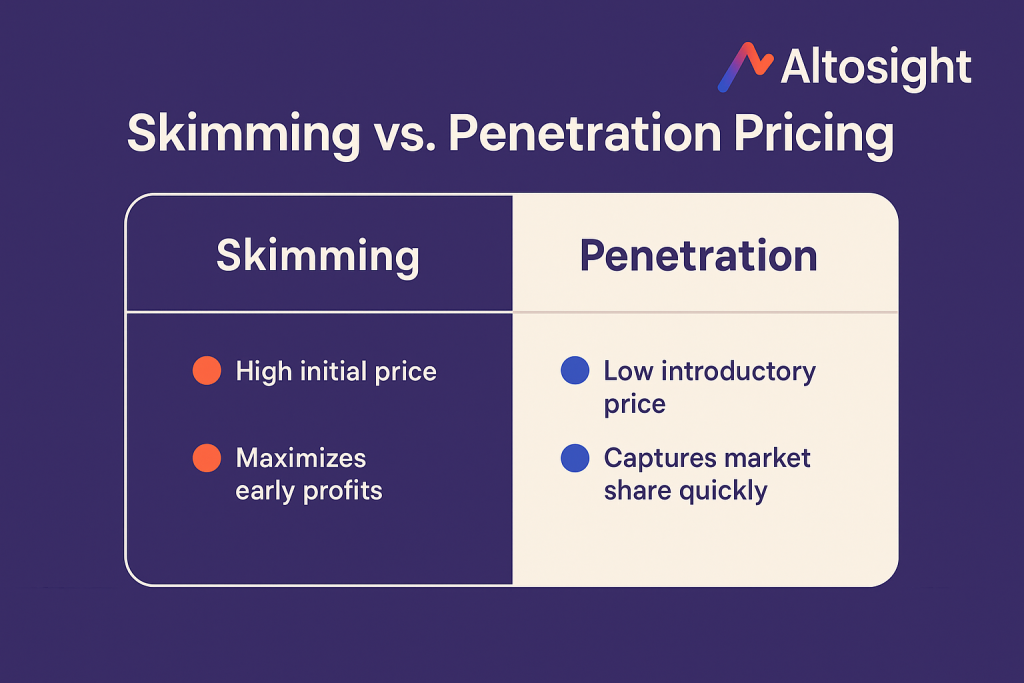
Skimming vs. Penetration Pricing
Imagine two coffee shops opening in your neighborhood. One charges $7 for a premium experience, gradually reducing to $4 over time. The other starts at $3 to pack the place with customers immediately.
That’s the fundamental difference between skimming and penetration pricing.
Penetration pricing looks to quickly capture market share through rock-bottom prices, sacrificing early profits for quick adoption. Skim pricing does the opposite—prioritizing immediate margins while accepting slower initial growth.
The choice between these strategies depends on several factors:
- Product uniqueness and innovation level
- Production capacity constraints
- Competitive landscape
- Brand positioning
- Target customer price sensitivity
Luxury brands almost always skim, while mass-market players typically penetrate. The most sophisticated companies know exactly when to use each approach.
When To Use Skimming Pricing
Your pricing strategy should match your market reality. A skimming pricing strategy works best under specific conditions:
- When your product offers genuine innovation or unique features that competitors can’t easily match.
- When specific customer segments value being first, they will pay accordingly.
- When your brand commands premium perception, price increases would damage credibility.
- When production capacity limits prevent you from immediately serving the entire market.
- When research and development costs were substantial and needed rapid recovery.
????Pro Tip: Skimming becomes riskier if your customers frequently compare prices or your product faces several similar alternatives. The strategy thrives on temporary uniqueness and customers willing to pay for it.
What Are the Benefits of Price Skimming?
Price skimming delivers powerful advantages when launching innovative products in competitive markets. From maximizing early profits to establishing premium positioning, these benefits explain why market leaders consistently choose this approach.
Rapid R&D Cost Recovery
Developing breakthrough products isn’t cheap.
The average pharmaceutical drug costs more than $2.5 billion to bring to market. A new smartphone platform requires hundreds of millions in development before a single unit sells.
Price skimming helps ease this financial pressure. Higher initial prices mean companies can recover their development investments faster, which is often essential when dealing with limited resources or ambitious innovation pipelines.
A startup that spent three years developing new technology might recover its entire investment within months through premium pricing, rather than waiting years at lower price points.
It creates a financial foundation for continued innovation that benefits everyone down the line.
Premium Brand Positioning & Margin Uplift
Your price tells customers more about your product’s value than any advertisement can.
When Apple launched the first iPad at $499 rather than $199, it wasn’t just maximizing profits—it was making a statement about the product’s quality and importance.
One of the most valuable advantages of price skimming is how it establishes and reinforces premium brand positioning. Products that launch at high prices automatically gain perception benefits:
- Customers assume superior quality and innovation
- The product becomes aspirational rather than merely functional
- Media coverage often emphasizes revolutionary capabilities rather than value considerations
- Higher margins enable exceptional customer service and premium packaging
These perception advantages persist even after prices decline, creating lasting brand value beyond immediate financial gains.
Market Segmentation & Early Feedback
Not all customers value products the same way or for the same reasons. Early adopters often care more about innovation and status than price, while mainstream buyers typically prioritize proven reliability and value. Budget consumers focus almost exclusively on affordability.
Price skimming allows you to serve these segments sequentially rather than simultaneously, creating powerful benefits:
- Early adopters provide valuable feedback before mass-market release
- Product refinements can address initial concerns before wider distribution
- Premium-segment usage patterns reveal unexpected opportunities or challenges
- Marketing messages can evolve based on real customer experiences
- Production can scale gradually rather than requiring immediate mass capacity
A camera manufacturer might discover that their professional customers value manual controls while mainstream users prefer automated features—insights that guide feature prioritization for different price tiers.
The Winning Formula:
| Benefit | Impact | Example |
| Rapid R&D Recovery | Faster reinvestment in innovation cycles | Tesla Model S profits funded Model 3 development |
| Premium Brand Positioning | Perceived quality and exclusivity | iPhone’s premium image persists despite lower-priced options |
| Segmented Market Capture | Sequential targeting of different buyers | Video game consoles are eventually reaching budget-conscious families |
| Controlled Production Scaling | Matching manufacturing to capabilities | New semiconductor technologies with limited initial yields |
| Early Adopter Insights | Real-world testing with the most engaged users | Professional software is refined before mainstream release |

What Are the Drawbacks of Price Skimming?
Every pricing strategy has potential pitfalls, and price skimming is no exception. If not carefully managed, the disadvantages of price skimming can undermine short-term profits and long-term market position.
Limited Volume & Elastic Demand
High prices mean fewer customers—it’s simple economics.
When implementing a price skimming strategy, you deliberately sacrifice early sales volume for higher per-unit profits. When this miscalculates market elasticity, problems can quickly snowball:
- Production economies of scale remain unrealized
- Market share growth stalls, creating competitive vulnerability
- Fixed costs spread across fewer units increase breakeven points
- Distribution partners may resist limited-volume products
A fitness equipment company launching a $3,000 smart treadmill might discover their market is smaller than projected, leaving inventory accumulating while competitors capture the mainstream segment with $1,200 alternatives.
The risk magnifies in price-sensitive categories or during economic downturns when consumer spending contracts. If market conditions shift, your premium strategy can quickly look tone-deaf.
Early Adopter Backlash & Fairness Perceptions
People hate feeling ripped off, especially loyal customers.
The psychology behind price skimming’s disadvantages often centers on perceived fairness. Early adopters can experience “buyer’s remorse” when prices drop shortly after launch, which damages brand relationships.
Take the release of the original iPhone. Just two months after launch, Apple slashed prices by $200, triggering widespread outrage from early adopters. The backlash forced Apple to offer $100 store credits as compensation.
The lesson? Consumer perceptions of fair pricing matter more than absolute price levels. The emotional response to perceived exploitation can create lasting damage, with consequences including:
- Negative social media amplification
- Reluctance to purchase future products at launch
- Diminished brand advocacy among previously loyal customers
- Expectations of rapid price drops affecting future purchasing decisions
Savvy companies implementing skimming strategies plan compensation mechanisms in advance—exclusive features, extended warranties, or bonus content that maintains value perception even as prices decline.
Competitive Entry & Inventory Risks
High margins attract competition like nothing else.
What are the drawbacks of price skimming?
The most significant is how it signals an opportunity to potential competitors. Your premium pricing essentially announces “substantial profits available here” to everyone watching your category.
When Samsung saw Apple’s healthy iPhone margins, they accelerated smartphone development. When generic pharmaceutical manufacturers see profitable medications, they prepare for patent expirations. When furniture retailers notice successful premium design stores, they create lower-priced alternatives.
Your skimming strategy needs to anticipate this competitive response, especially when:
- Barriers to entry are relatively low.
- Your innovations lack strong intellectual property protection.
- Large competitors with substantial resources monitor your category.
- Your margins exceed industry norms by significant percentages.
Inventory management further complicates matters as prices decline. Products purchased at higher wholesale costs become progressively less profitable, creating internal tension between finance and sales departments.
Real-World Examples of Price Skimming
Top brands often use price skimming every day without consumers even realizing it. Let’s look at how real companies implement this strategy to maximize profits while expanding their market reach.
Apple iPhone Launch
Few companies execute price skimming as masterfully as Apple.
When the original iPhone launched in 2007, its $499-$599 price (with contract) was a massive premium over typical smartphones. Critics questioned whether consumers would pay computer-level prices for phones.
The answer came quickly: yes, they would—at least the innovation-seeking early adopters.
What followed demonstrated a perfect skimming pricing strategy:
- Initial premium pricing captured early adopter enthusiasm and established the product as revolutionary.
- Gradual price reductions expanded market access while maintaining premium positioning.
- Introduction of previous-generation models at lower price points reached price-sensitive segments.
- New models maintained premium price points while adding features that justified renewed skimming.
Even today, Apple introduces cutting-edge features like advanced cameras and processing capabilities in premium-priced Pro models before eventually incorporating them into standard iPhones, continuing the skimming approach across product tiers.
Tesla Model S Roll-out
Tesla’s journey from niche luxury to mainstream electric vehicles is textbook price skimming.
In 2012, the Model S launched with configurations ranging from $57,400 to over $100,000, targeting wealthy early adopters who valued innovation and status. These premium prices funded operations and the development of more affordable vehicles.
As Tesla’s skim pricing tactics progressed:
- Production efficiencies reduced manufacturing costs.
- Battery technology improvements lowered a major component expense.
- Brand reputation and charging network development created additional value.
- New models at lower price points expanded market reach.
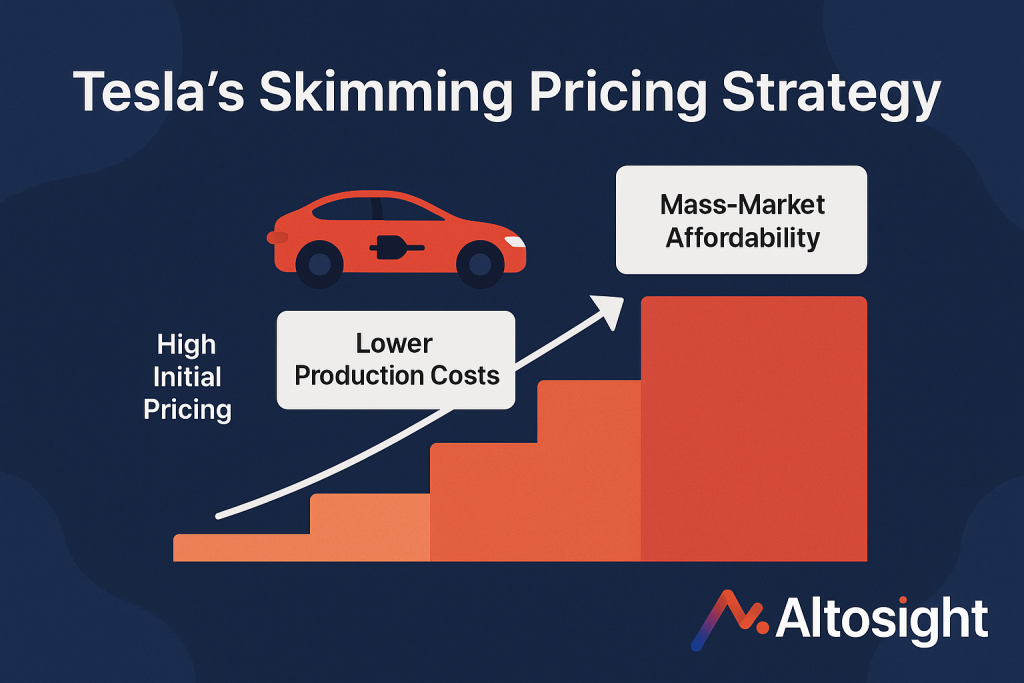
The Model 3 launch at $35,000 (eventually $38,990) was the culmination of this planned descent, reaching mainstream consumers while maintaining premium positioning relative to comparable gas vehicles.
Tesla’s approach shows how effective skimming strategies consider the entire product ecosystem rather than individual product pricing in isolation.
Other Niches: Pharma, Gaming Consoles
What companies use price skimming? Look almost anywhere, and you’ll find the strategy:
- Sony and Microsoft routinely launch gaming consoles at premium prices ($499+) before introducing slim versions and price reductions over the product lifecycle
- Pharmaceutical companies need to implement skimming under patent protection, with prices dropping substantially when generic alternatives emerge.
- Fashion brands release collections at full retail before sequential markdowns through outlet channels.
- Publishers release hardcover books at premium prices before paperback editions reach price-sensitive readers.
The pharmaceutical example of price skimming highlights both benefits and ethical considerations.
Initial premium pricing funds critical research, but raises significant access concerns for life-saving medications—showing why skimming strategies require careful consideration beyond pure profit maximization.
Advanced & Hybrid Skimming Strategies
Companies today are taking price skimming beyond its basic form with innovative approaches. These modern strategies blend traditional skimming with other pricing techniques to create more flexible and responsive systems that maximize profits across all customer segments.
AI-Enabled Dynamic Skimming
Traditional price skimming followed predetermined reduction schedules. Modern approaches leverage real-time data and artificial intelligence to optimize every phase of the strategy.

AI-enabled dynamic skimming continuously monitors and responds to:
- Actual vs. projected sales volumes at each price point
- Competitive pricing movements and new market entrants
- Inventory positions across distribution channels
- Consumer sentiment and demand signals
- Macroeconomic indicators affecting purchasing power
Unlike rigid traditional approaches, these systems might accelerate price reductions when demand elasticity exceeds projections or delay reductions when sales remain strong at current price points.
Major retailers and electronics manufacturers have increasingly adopted algorithmic pricing tools that can analyze thousands of data points to determine the optimal timing for price adjustments.
These AI systems identify exactly when to drop prices to maximize total revenue across a product’s entire lifecycle.
????Pro Tip: Start small with dynamic skimming by testing AI-recommended price adjustments on limited product lines before expanding to your core offerings. This provides valuable learning while minimizing risk to established revenue streams.
Subscription & Freemium Skimming
Software companies have reimagined skimming for the subscription economy.
Rather than reducing absolute prices over time, they create tiered subscription offerings where premium capabilities gradually migrate to lower-priced tiers as newer innovations launch at premium levels.
Adobe’s Creative Cloud perfectly illustrates this approach. Features initially available only in premium tiers eventually reach standard subscriptions, while cutting-edge capabilities like AI-powered editing tools remain premium-exclusive until innovations take their place.
Freemium models are another variation. They offer basic functionality for free while charging premium prices for advanced features. Over time, previously premium features may become free while new premium capabilities maintain the revenue stream.
Combining Skimming With Bundling
Innovative companies increasingly combine price skimming with strategic bundling to enhance perceived value while maintaining premium pricing.
Rather than directly dropping prices, they initially bundle premium products with exclusive services, complementary products, or extended warranties.
As the product matures, these bundles gradually unbundle, effectively reducing prices without explicitly cutting the product’s price tag.
Examples include:
- Luxury vehicle manufacturers include premium maintenance packages with new models before making these separately purchasable.
- Enterprise software vendors initially bundle implementation services before transitioning to separate service fees.
- Smart home companies include premium subscriptions with device purchases before making these optional.
This approach preserves price integrity perceptions while accomplishing the same market expansion objectives as traditional skimming.
Industry-Specific Playbooks
Price skimming looks different across industries due to unique market dynamics and customer expectations. From software subscription models to fashion’s seasonal cycles, these tailored approaches show how to adapt skimming principles to your specific business context.
SaaS & Software
Software companies face unique pricing challenges—near-zero marginal production costs combined with substantial development investments and ongoing support requirements.
For SaaS companies, effective skimming strategies typically involve:
- Feature-based tiering rather than direct price reductions.
- Enterprise-first approaches that capture high-value organizational customers before addressing smaller businesses.
- Bundled implementation and training services during the early phases.
- Gradual expansion of free tier capabilities as premium features evolve.
The most sophisticated software companies maintain persistent innovation pipelines that enable continuous premium positioning of the newest capabilities while systematically expanding standard feature sets.
Hardware & Consumer Electronics
Electronics manufacturers face different challenges—component costs that naturally decline over time, production efficiencies that improve with scale, and competitive pressure from fast followers.
Effective skimming pricing examples in consumer electronics include:
- Sequential geographic rollouts that capture premium-paying markets first
- Limited edition initial releases with premium materials or capabilities
- Bundle-based transitioning that maintains price points while adding value
- Generation-based strategies where previous models remain available at lower price points
Television manufacturers exemplify this approach, introducing technologies like 4K resolution or OLED panels at premium prices before systematically incorporating them into mid-tier and eventually budget models as newer innovations (8K, microLED) restart the premium cycle.
Fashion & Luxury Goods
Fashion brands have practiced price skimming for ages, though they rarely use the term.
The standard fashion cycle follows a predictable pattern:
- Runway collections introduce innovations at maximum price points
- Main collections reach department stores at premium retail prices
- Mid-season sales offer the first price reductions to expand accessibility
- End-of-season clearance and outlet availability complete the cycle
- Archive status potentially creates secondary market premium pricing
Luxury brands extend this approach through diffusion lines that bring watered-down versions of premium design elements to progressively more affordable price points, maintaining brand prestige while capturing revenue from price-sensitive segments.
Pharma & Healthcare
Few industries demonstrate the complexities of price skimming more clearly than healthcare. Pharmaceutical companies routinely launch breakthrough medications at premium prices, gradually reducing them as patent protection expires and generic competition emerges.
The ethical dimensions here extend beyond typical consumer products—pricing strategies directly impact health outcomes and access to care. Responsible skimming approaches in healthcare:
- Provide patient assistance programs for those unable to afford the initial pricing
- Establish transparent price reduction schedules aligned with development cost recovery
- Consider global access implications, particularly for essential treatments
- Balance innovation funding with ethical access considerations
These complexities make healthcare pricing uniquely sensitive—where strategic decisions must balance innovation incentives with affordability, regulatory compliance, and public trust.
Tools, Templates & Interactive Resources
Implementing effective price skimming requires careful analysis and ongoing optimization. At Altosight, our interactive resources help simplify the process:
- Skimming Curve Calculator: Model different initial price points and reduction schedules to visualize revenue, profit, and volume projections under various scenarios.
- Competitor Response Simulator: Estimate likely competitive reactions to your pricing strategy and their potential impact on your results.
- Customer Segmentation Tool: Identify and quantify different customer segments to optimize price reduction timing for maximum lifetime revenue.
- Dynamic Pricing API: Connect your inventory and sales systems to Altosight’s AI pricing engine for real-time skimming optimization.
These tools turn theoretical skimming concepts into practical implementation plans tailored to your specific market conditions and business objectives.
Perfect Your Price Skimming Strategy With Altosight
Price skimming isn’t just a pricing tactic—it’s a strategic approach to maximizing the lifetime value of innovation. When implemented thoughtfully, businesses can recover development costs quickly while systematically expanding market reach.
The most successful strategies balance short-term profit objectives with long-term market development goals, creating sustainable advantages rather than temporary gains.
Altosight’s Competitor Price Monitoring spots market shifts as they happen, enabling perfectly timed adjustments at every product lifecycle stage.
Our Dynamic Pricing algorithms optimize price points based on real-time data, while MAP Monitoring preserves your pricing integrity across all channels. When competitors enter your space, Assortment Tracking gives you early warning to adjust before your margins suffer.
Whether launching a revolutionary product or rethinking existing pricing approaches, our platform turns complex strategy into confident execution. Ready to take your pricing to the next level? Contact us to learn more about implementing a dynamic pricing strategy or schedule a demo with our pricing experts.
What’s your biggest challenge with implementing price skimming in your business? We’d love to hear about your experience in the comments below!